The Data Architecture Systems and Standards for Africa (DASSA)
Project Period
August 2025 - August 2025
1.1 Background
The field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has seen significant advancements in recent years, bringing about opportunities to leverage large amounts of structured and unstructured data for the public good and health. As data becomes increasingly digitized and recognized as a public good, there is a growing need to share this data safely and responsibly. One significant gap is the lack of capacity among African researchers to access and utilize high-quality research data. Due to limited training and resources for data management and analysis, researchers often struggle to leverage existing datasets for their research fully. By providing a platform like DASSA, African researchers can gain access to a centralized, harmonized, and curated database of high-quality datasets, promoting collaboration and knowledge sharing within the scientific community.
Infrastructure is another challenge in many African countries, with limited internet connectivity and computing resources hindering the sharing and utilization of research data. DASSA addresses this issue by offering a user-friendly platform that is accessible even in low-resource settings. This ensures that African researchers have the necessary infrastructure to access and utilize data for their research.
African researchers often lack autonomy and control over the data they generate. Currently, data produced by African scientists usually ends up in the hands of external organizations and researchers, limiting the ability of African researchers to fully leverage their data for further research and development. DASSA, as an African-led and African-based platform, empowers African scientists by giving them autonomy and control over their data. This promotes ownership and ensures that African researchers can fully benefit from their data, leading to more impactful research outcomes.
There is a limited data-sharing culture in many African research institutes, where data-sharing practices are not well-established or encouraged. This lack of culture hinders collaboration and slows down the progress of research. DASSA promotes a data-sharing culture in Africa by providing incentives and recognition for data sharing. In addition, the in-built reward system incentivizes researchers to share their data, leading to increased data availability and reuse among African researchers.
Research datasets in Africa are often fragmented and inaccessible. These datasets are scattered across different institutions, making it challenging for researchers to find and access relevant datasets for their research. The DASSA platform allows for easy pulling of datasets from other platforms through API endpoints, makes pulled datasets available to researchers, and provides a user-friendly experience for data retrieval, ensuring that African researchers have easy access to relevant and reliable datasets.
1.2 The DASSA Platform
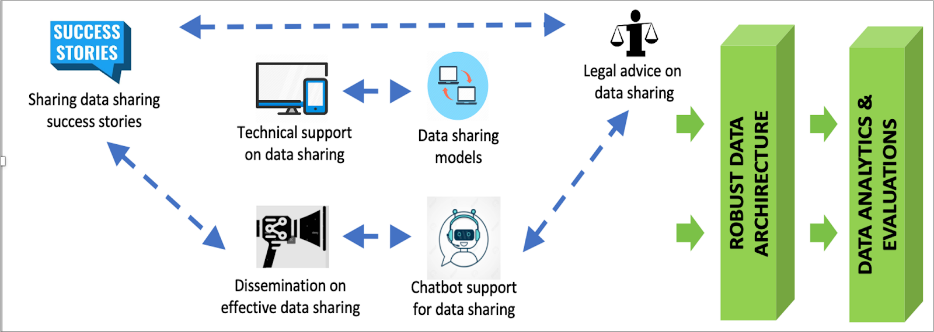
The Data Architecture Systems and Standards for APHRC (DASSA) is a platform that aims at collecting, curating, and standardizing research data from institutions across the continent, anchored in the principles of open science, collaboration, and guided by FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) principles, while adhering to African data governance frameworks and laws. The DASSA architecture is summarized in Figure 1. It can be categorized into several key areas: data assessment and documentation, data preservation and accessibility, collaboration and engagement, platform development and refinement, data governance and ethics, capacity building and training, integration of open data science principles, African-led and African-based approach, collaboration and interdisciplinary research, recognition and incentives, real-time updates, and ethical, legal, and social considerations.
These areas focus on assessing and documenting existing datasets, preserving data and making it accessible, engaging with researchers and stakeholders, developing and refining the platform, ensuring ethical data use, building capacity, promoting open science principles, involving African researchers, fostering collaboration and interdisciplinary research, providing recognition and incentives, maintaining real-time updates, and addressing ethical and legal considerations.
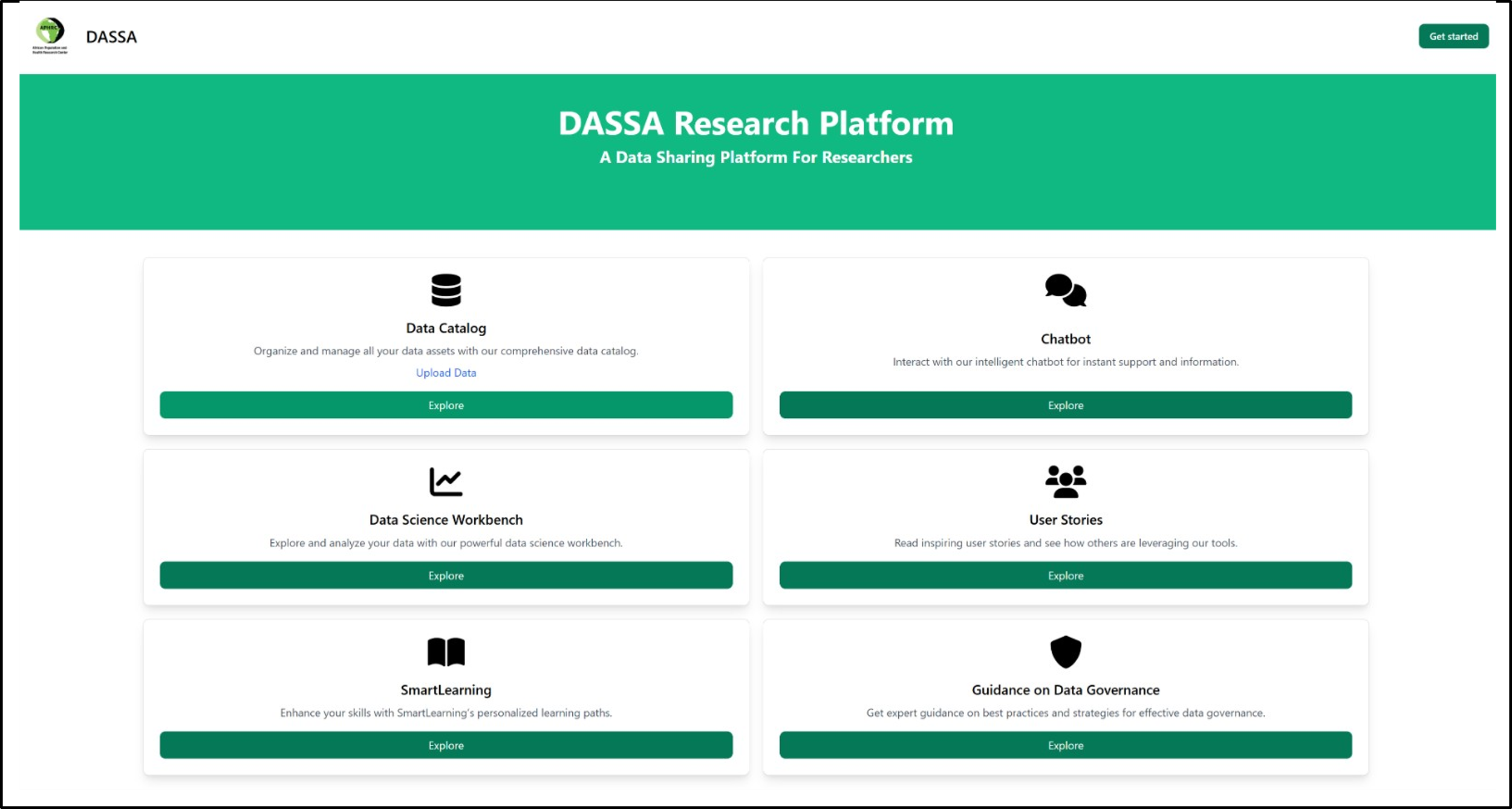 DASSA is built on an open-source, scalable infrastructure utilizing Ubuntu as the base operating system and CloudStack for cloud resource management. It is built on a scalable microservices architecture, shown in Figure 2, and integrates a suite of functionalities designed to support collaborative and data-driven research across Africa. Its Data Catalog allows institutions and researchers to securely organize, manage, and share datasets within a trusted research environment and promotes the discoverability and reuse of data. The platform’s Data Science Workbench supports advanced data exploration, transformation, and analysis, and includes low- and no-code tools that enable users to apply machine learning techniques with ease. To enhance user engagement and support, DASSA incorporates an AI-powered chatbot that provides immediate assistance and guidance. Additionally, the SmartLearning module delivers personalized, adaptive learning paths that help users develop and strengthen their data science competencies. The platform also offers comprehensive advice on data governance, ensuring compliance with regional legal requirements and promoting ethical data stewardship.
DASSA is built on an open-source, scalable infrastructure utilizing Ubuntu as the base operating system and CloudStack for cloud resource management. It is built on a scalable microservices architecture, shown in Figure 2, and integrates a suite of functionalities designed to support collaborative and data-driven research across Africa. Its Data Catalog allows institutions and researchers to securely organize, manage, and share datasets within a trusted research environment and promotes the discoverability and reuse of data. The platform’s Data Science Workbench supports advanced data exploration, transformation, and analysis, and includes low- and no-code tools that enable users to apply machine learning techniques with ease. To enhance user engagement and support, DASSA incorporates an AI-powered chatbot that provides immediate assistance and guidance. Additionally, the SmartLearning module delivers personalized, adaptive learning paths that help users develop and strengthen their data science competencies. The platform also offers comprehensive advice on data governance, ensuring compliance with regional legal requirements and promoting ethical data stewardship.
For more details, log on to the DASSA Platform.